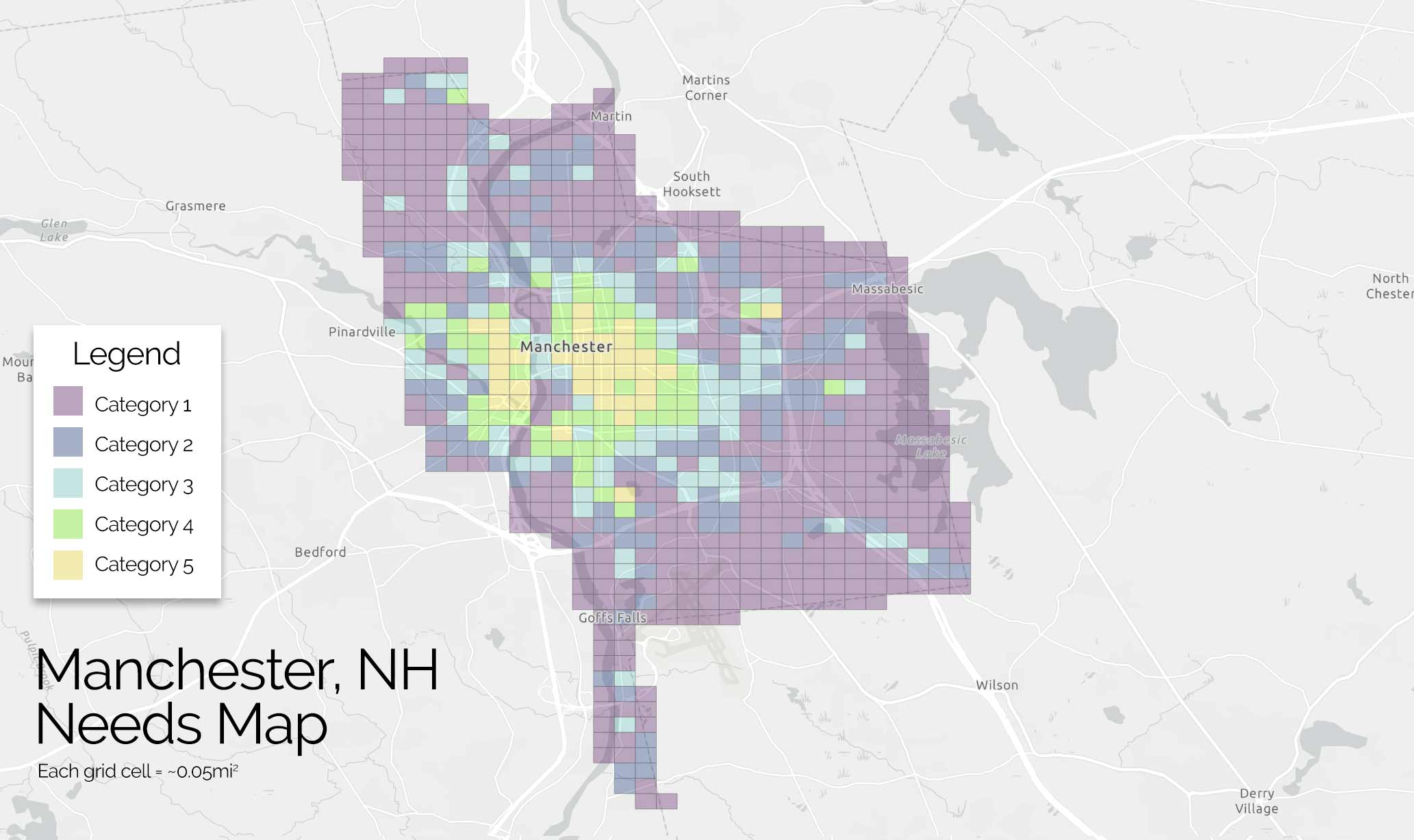
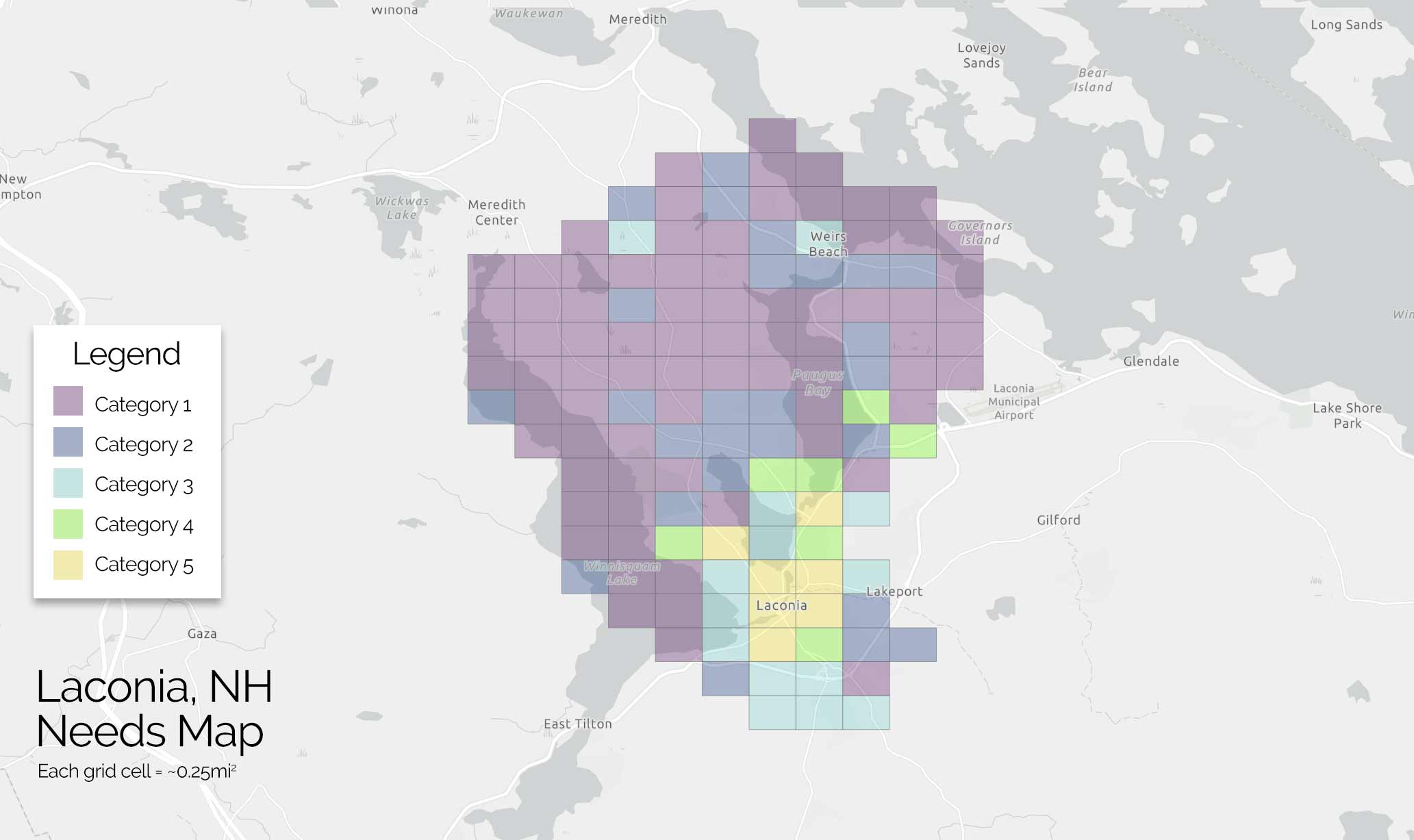
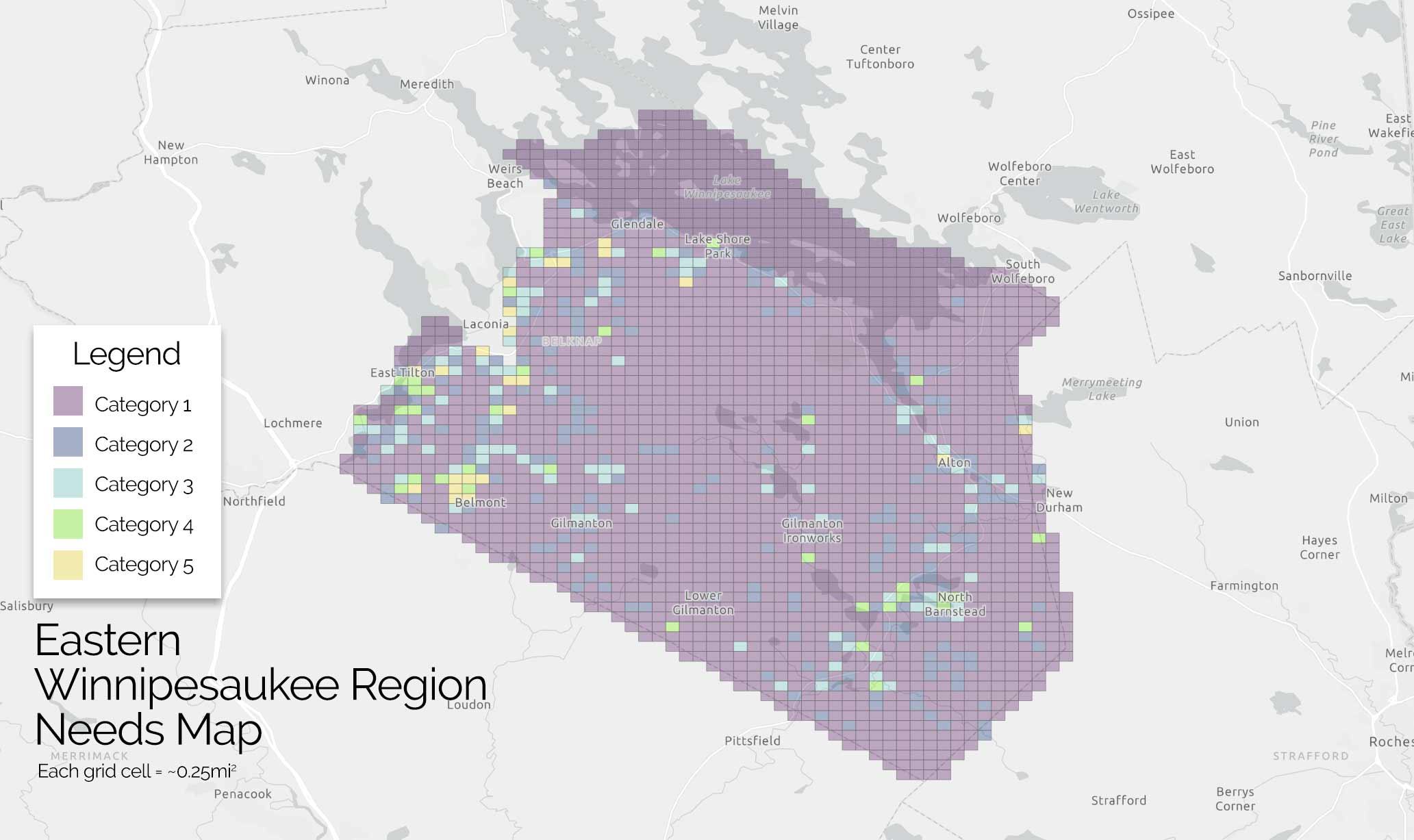
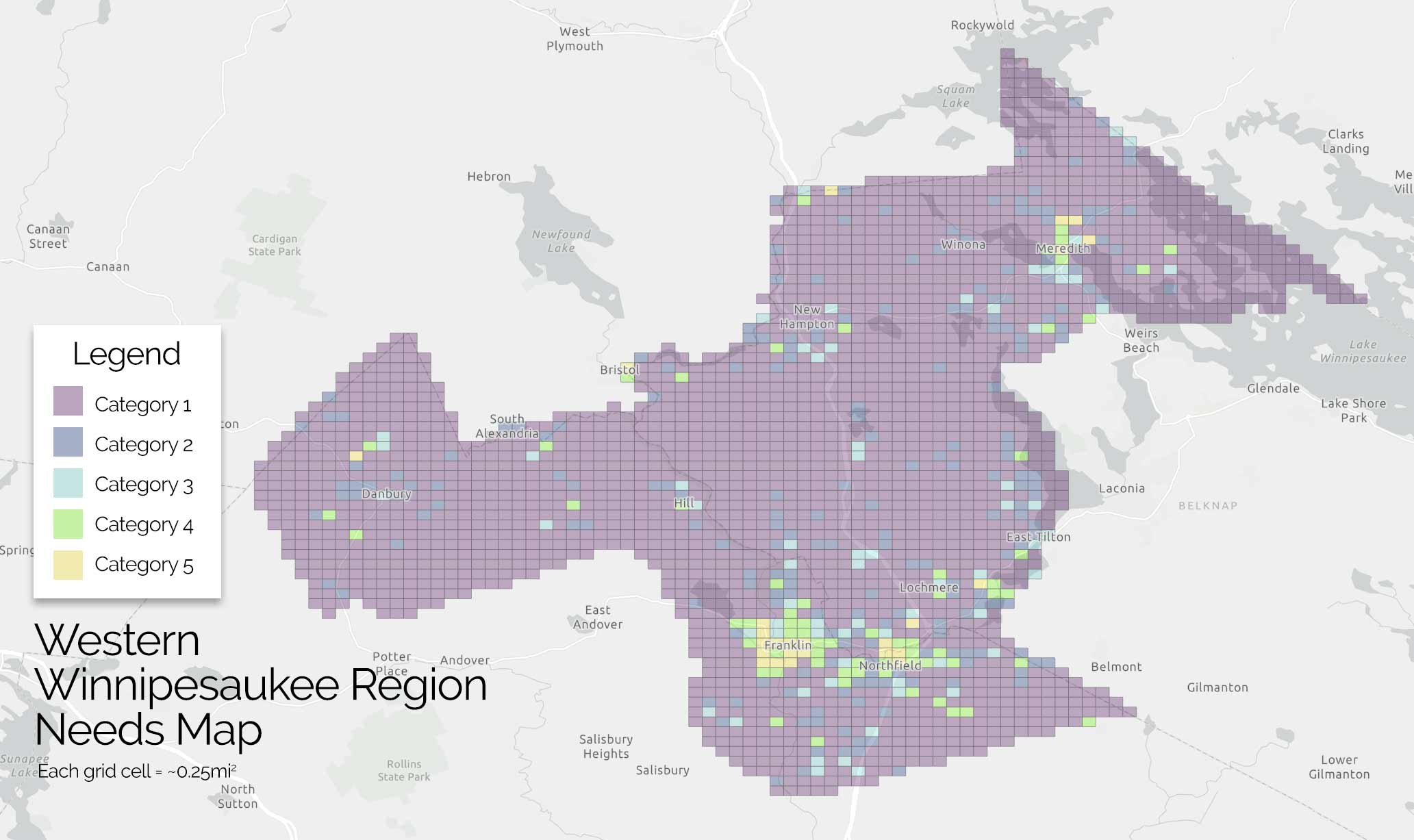
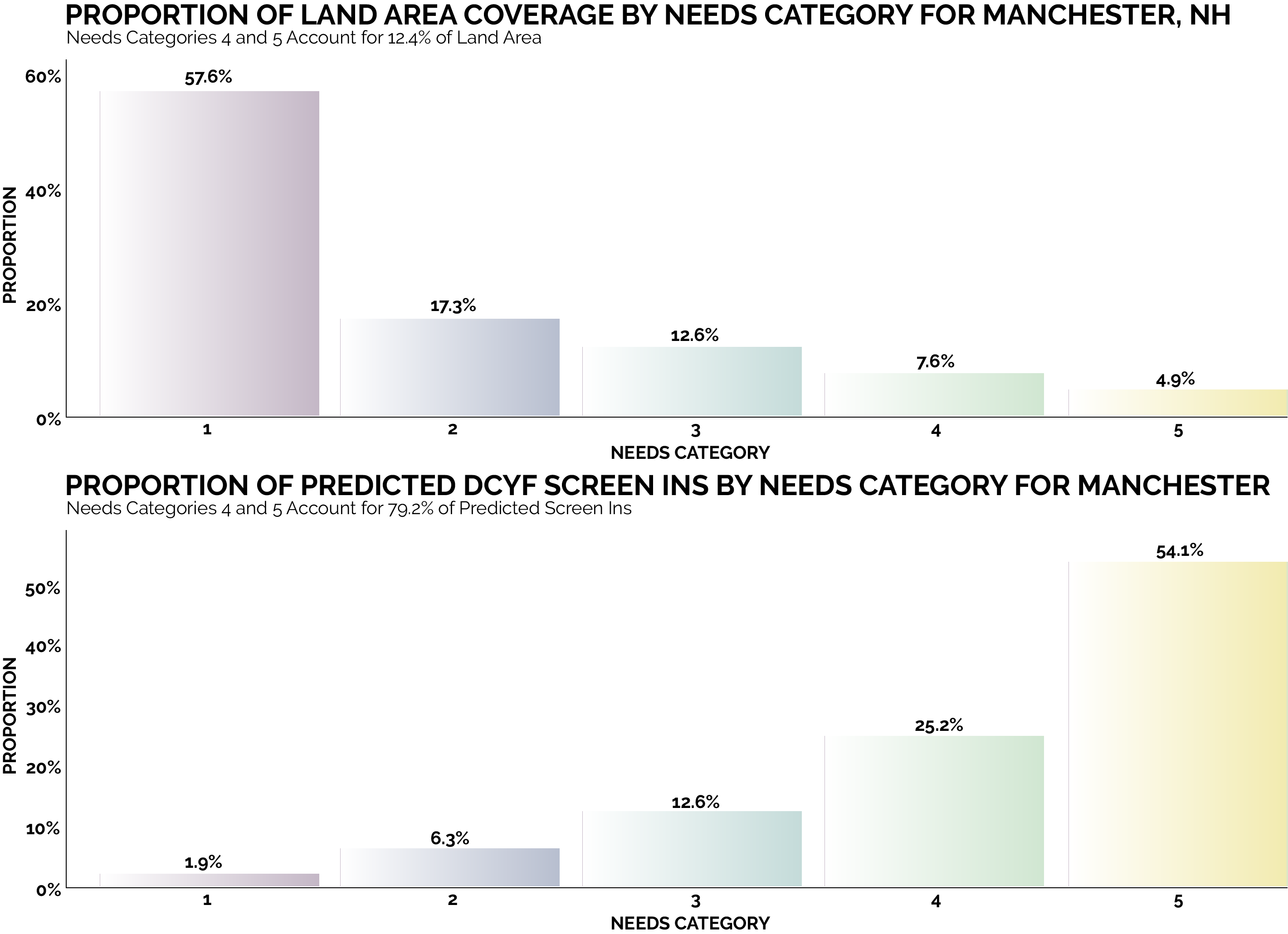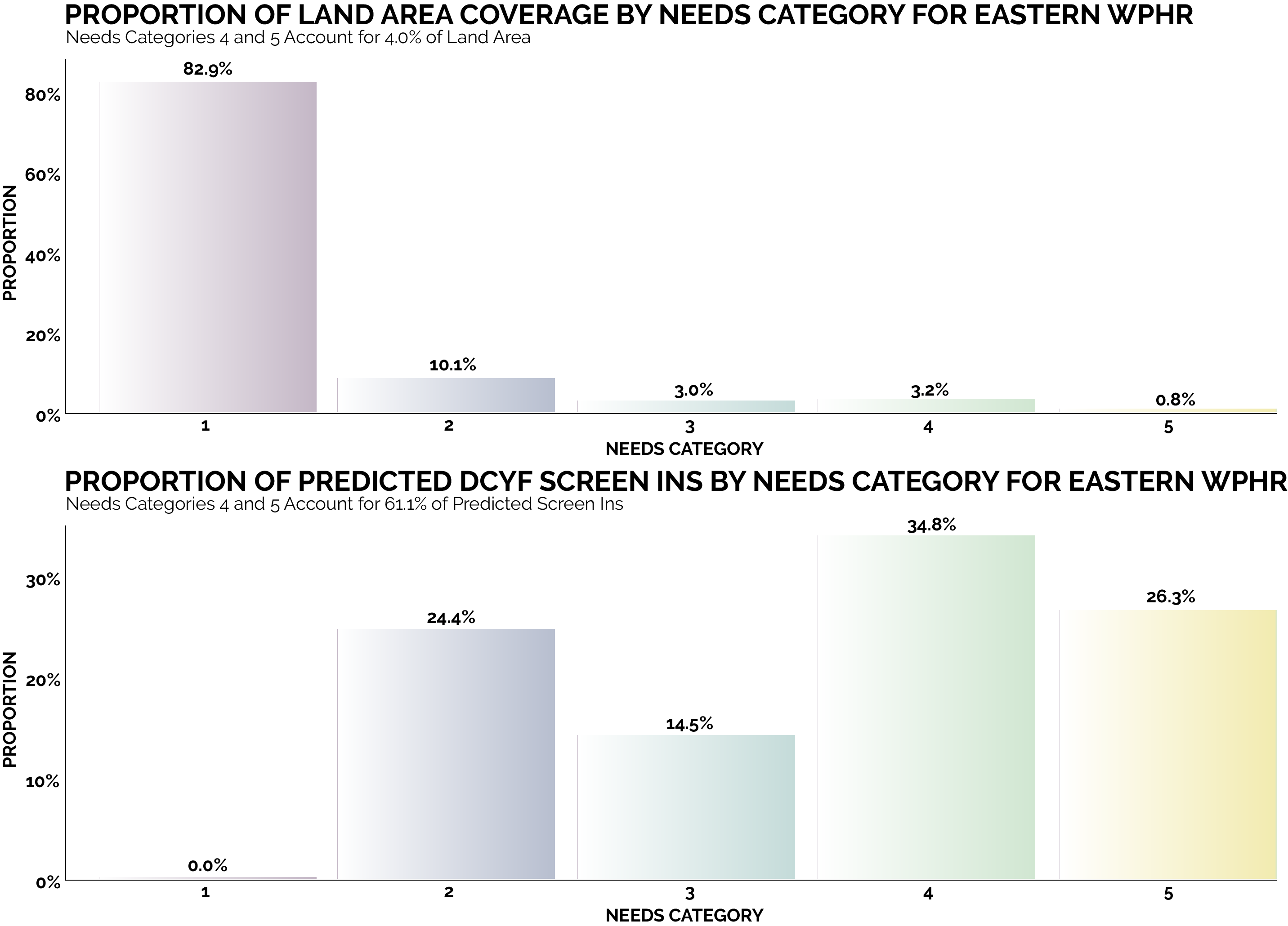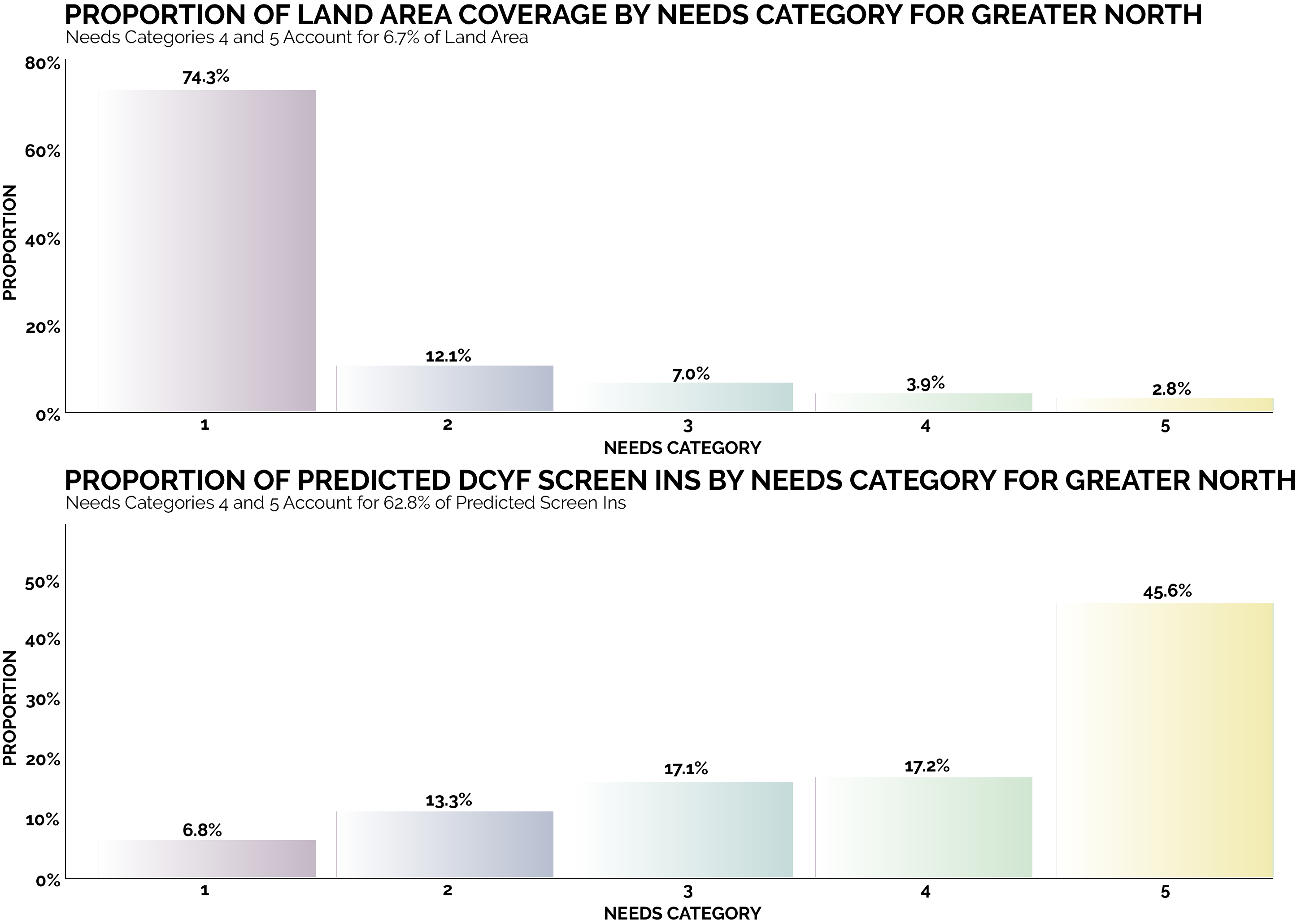Analysis Data Included
- Child Protection: screened-in allegation reports, founded assessments, removals, provider/foster homes
- Juvenile Justice: removals, petitions filed, petitions found true
- Hospital Discharge: emergency department visits and hospitalizations -- substance use, intentional injury, assault, prevention quality indicators
- Childhood Lead Poisoning
- Vital Records: child mortality, premature death, suicide, homicide
- New Heights: service eligibility
- See Click Fix: community non-emergency logger, parking enforcement, graffiti, abandoned furniture, nonemergency police
- OpenStreetMap points of interest: laundries, bars, supermarkets, places of worship, hospitals, fire stations, libraries, courts, convenience stores
The goal behind the modeling process is to use the observed data around maltreatment experiences and test whether those experiences are common to places where maltreatment may occur but are not directly observed. This is done by using data associated with ‘neighborhood effects’ (individual, family, and household-level factors) that may be influencing maltreatment, such as substance use, education neglect, poverty, among others.
This process helps balance factors that are unique to certain regions and factors that are common to multiple regions; finding this balance segregated by common areas, or areas with similar factors, is important to assist making decisions confidently.
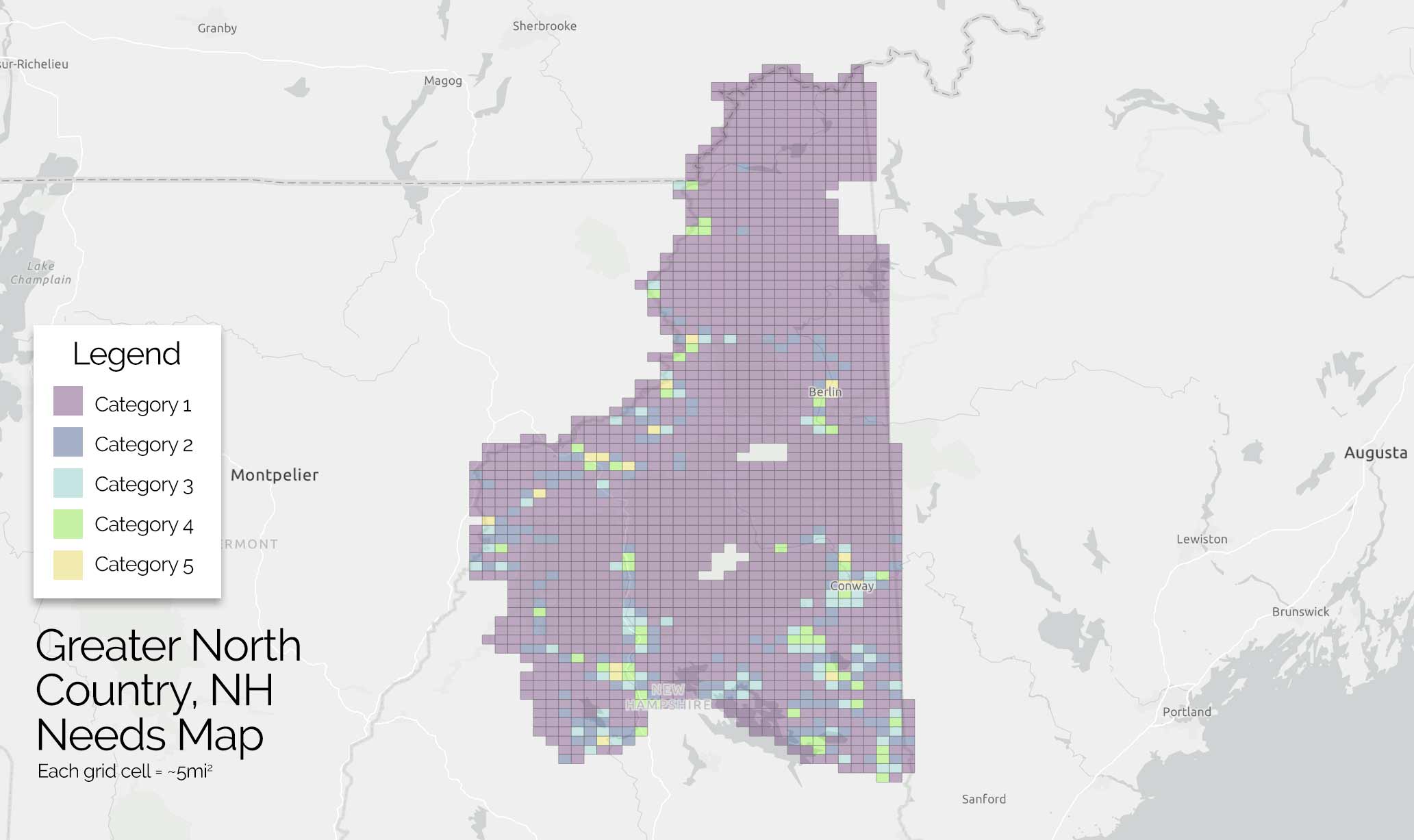
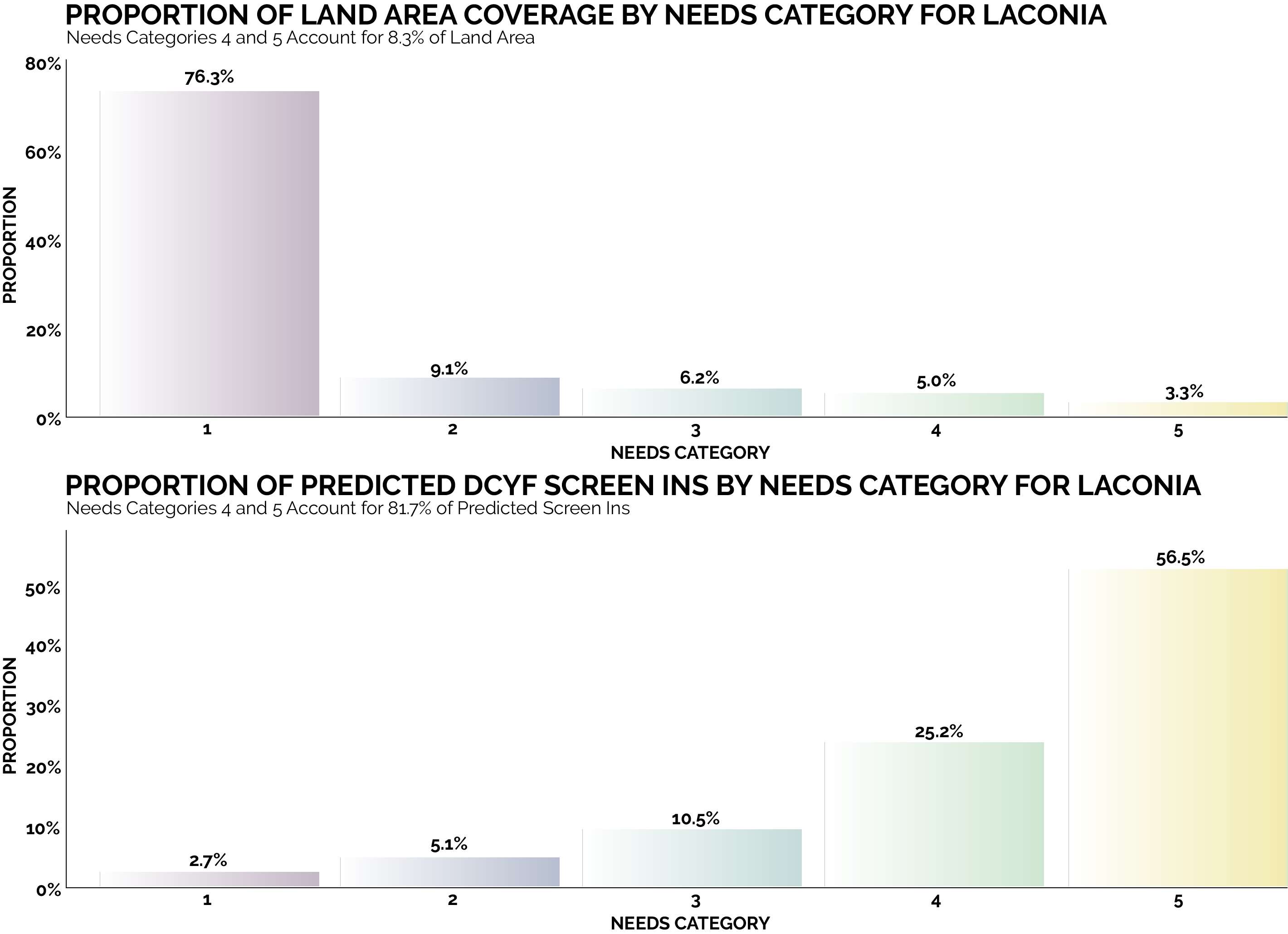
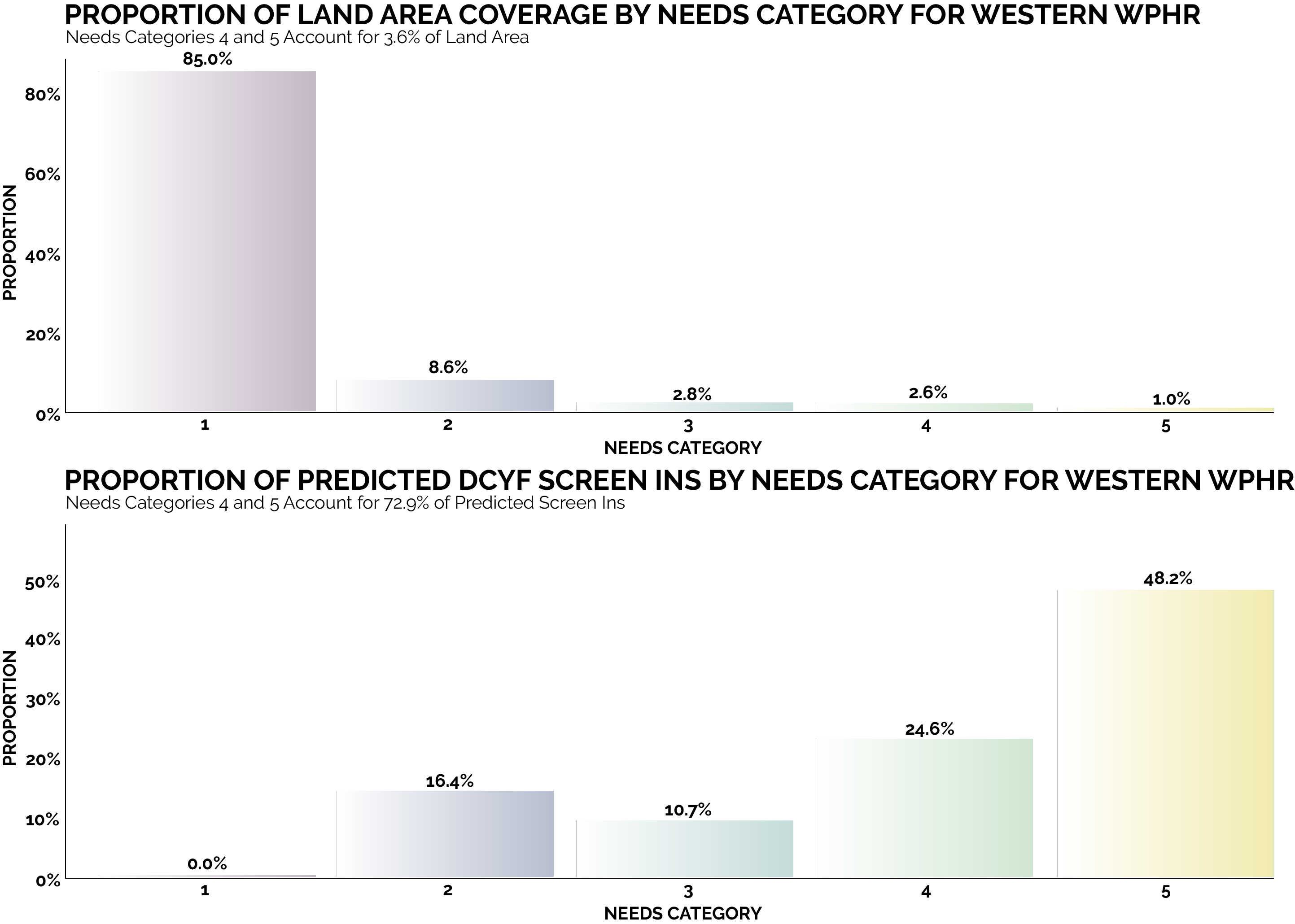
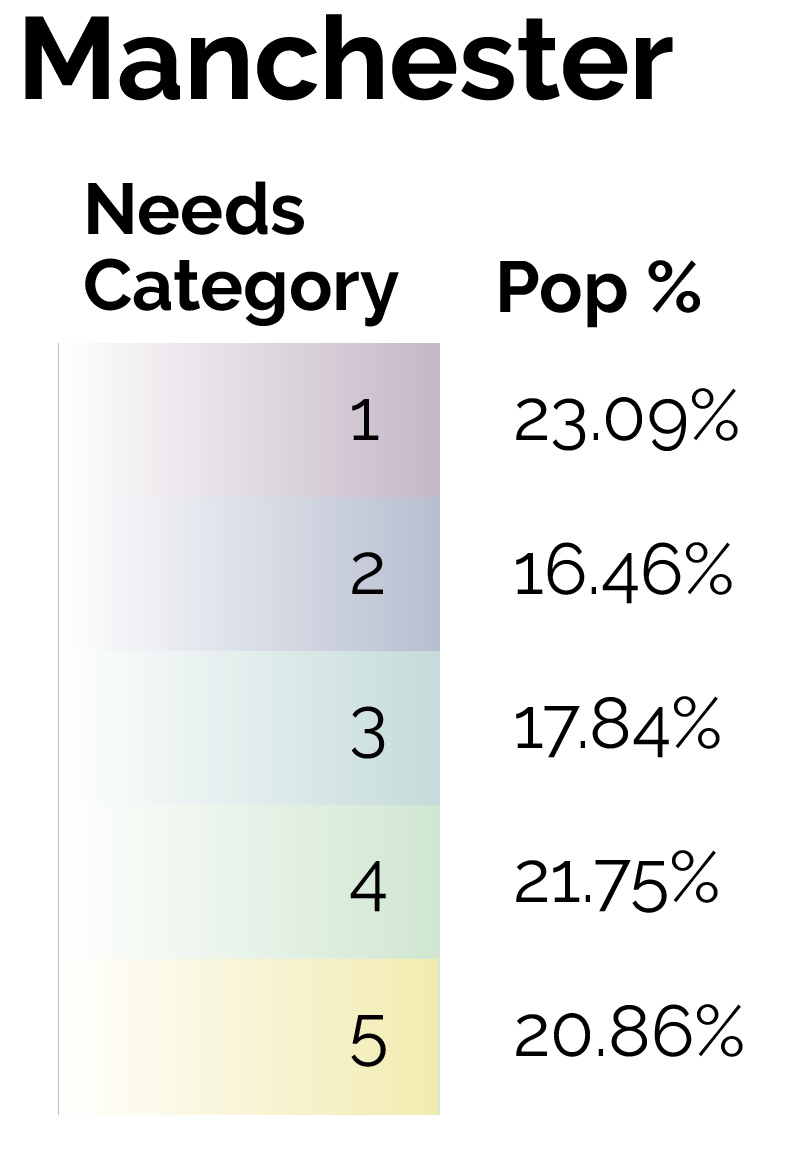
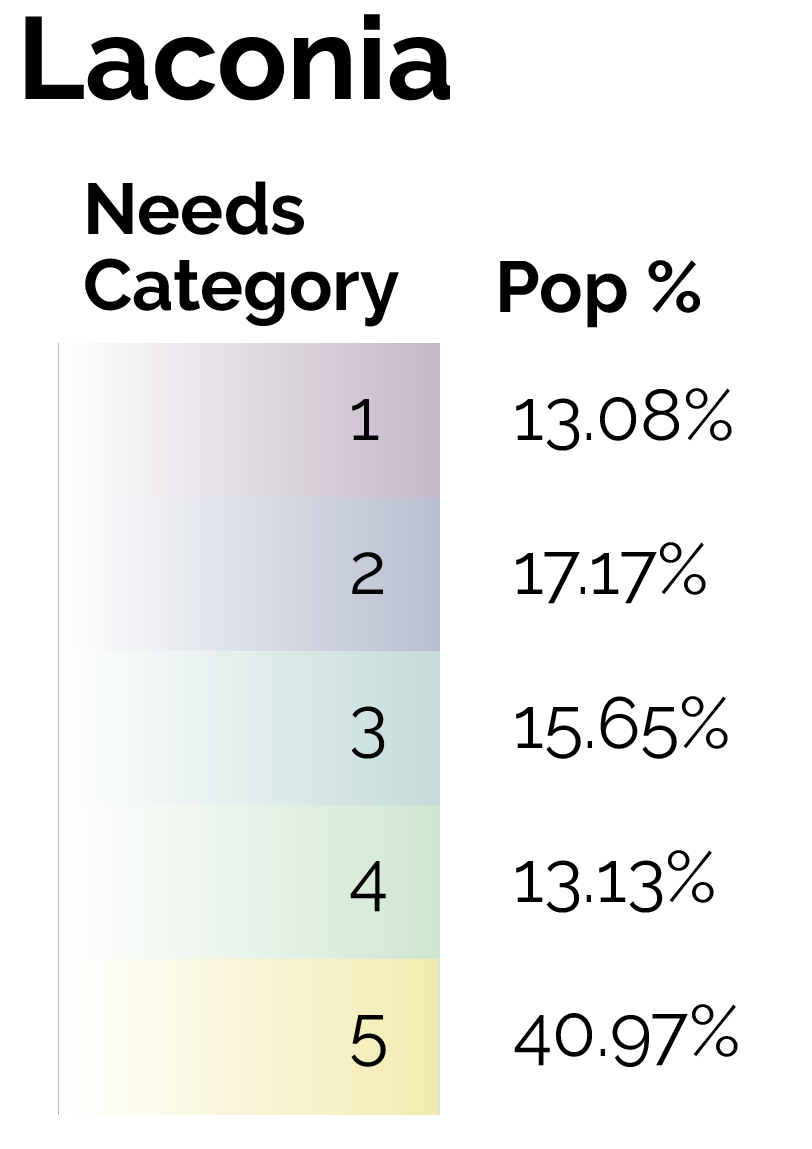
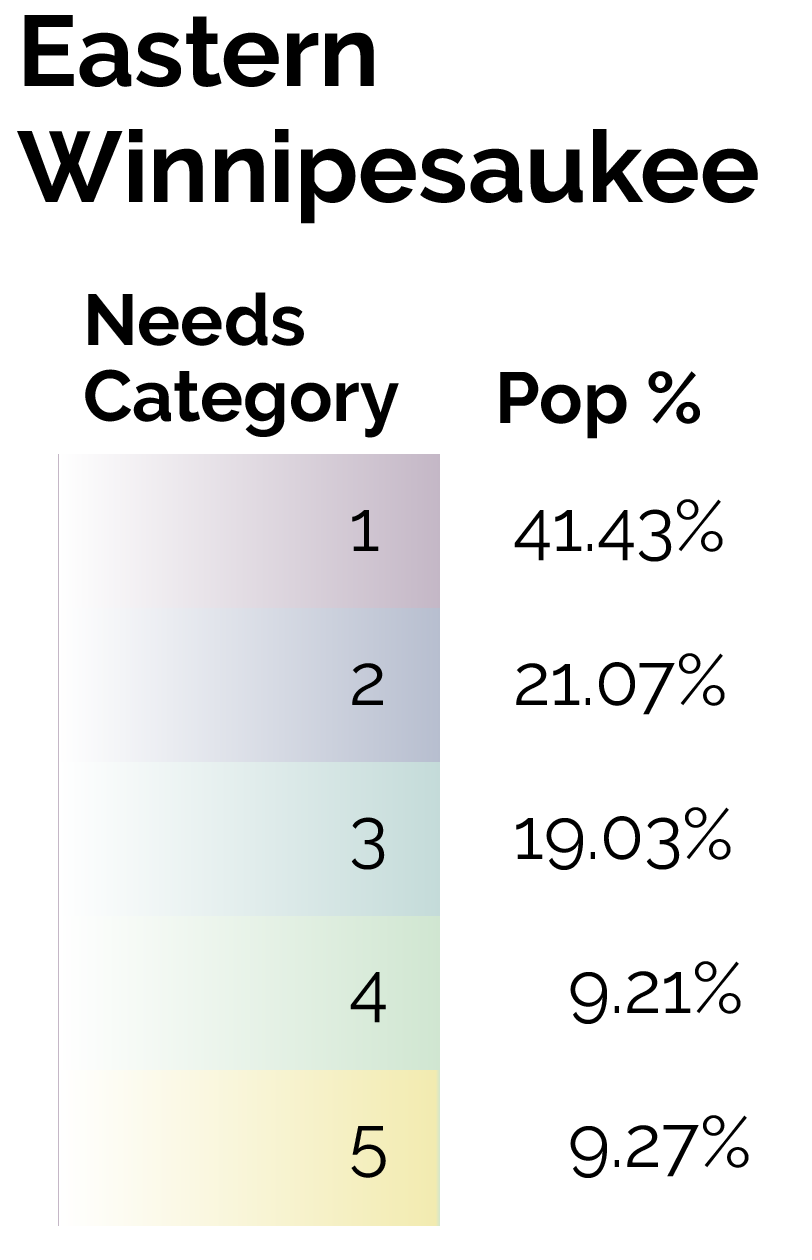
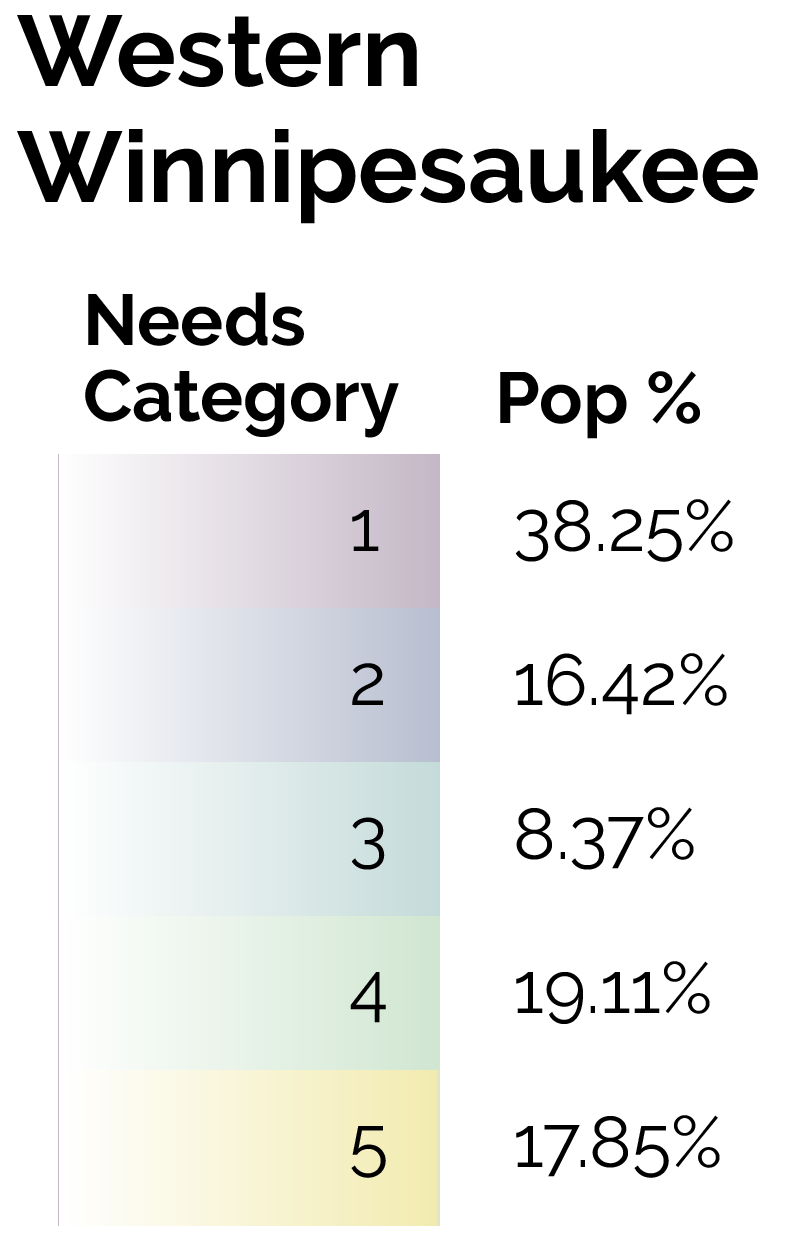
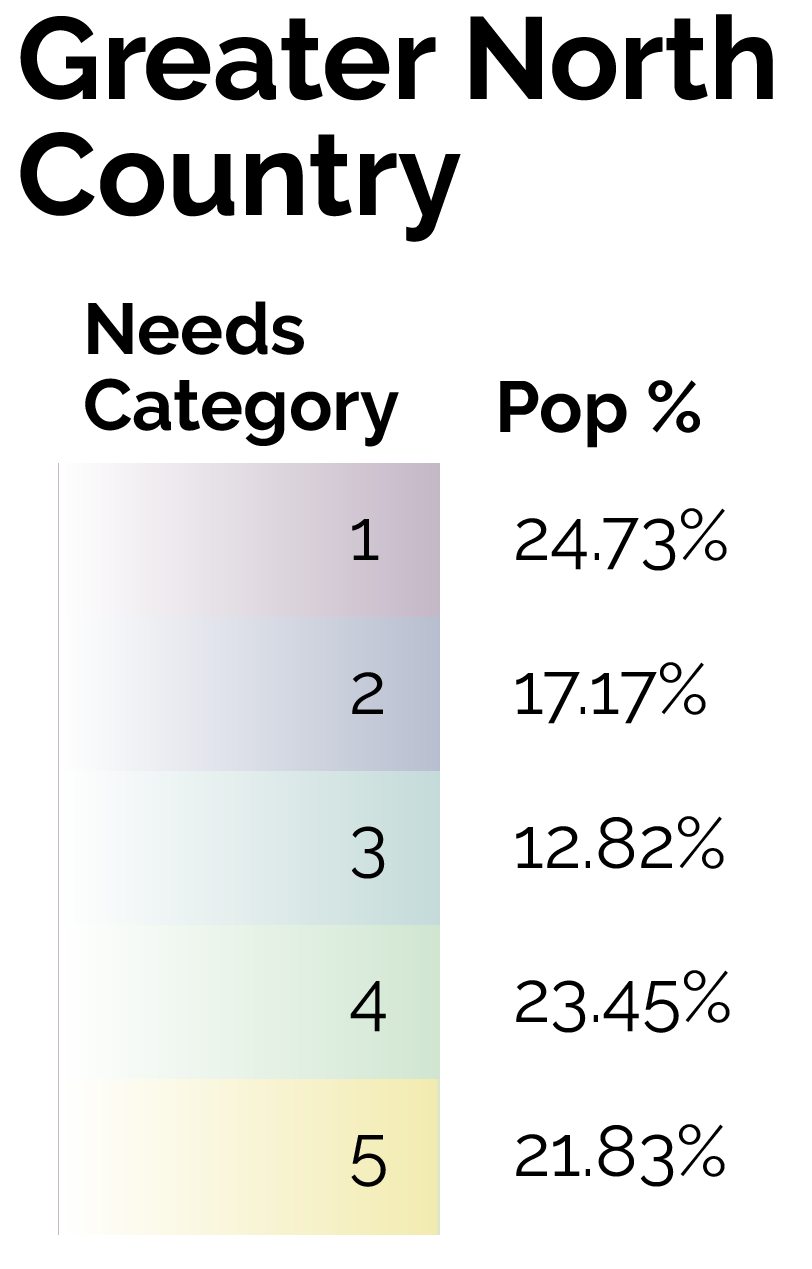
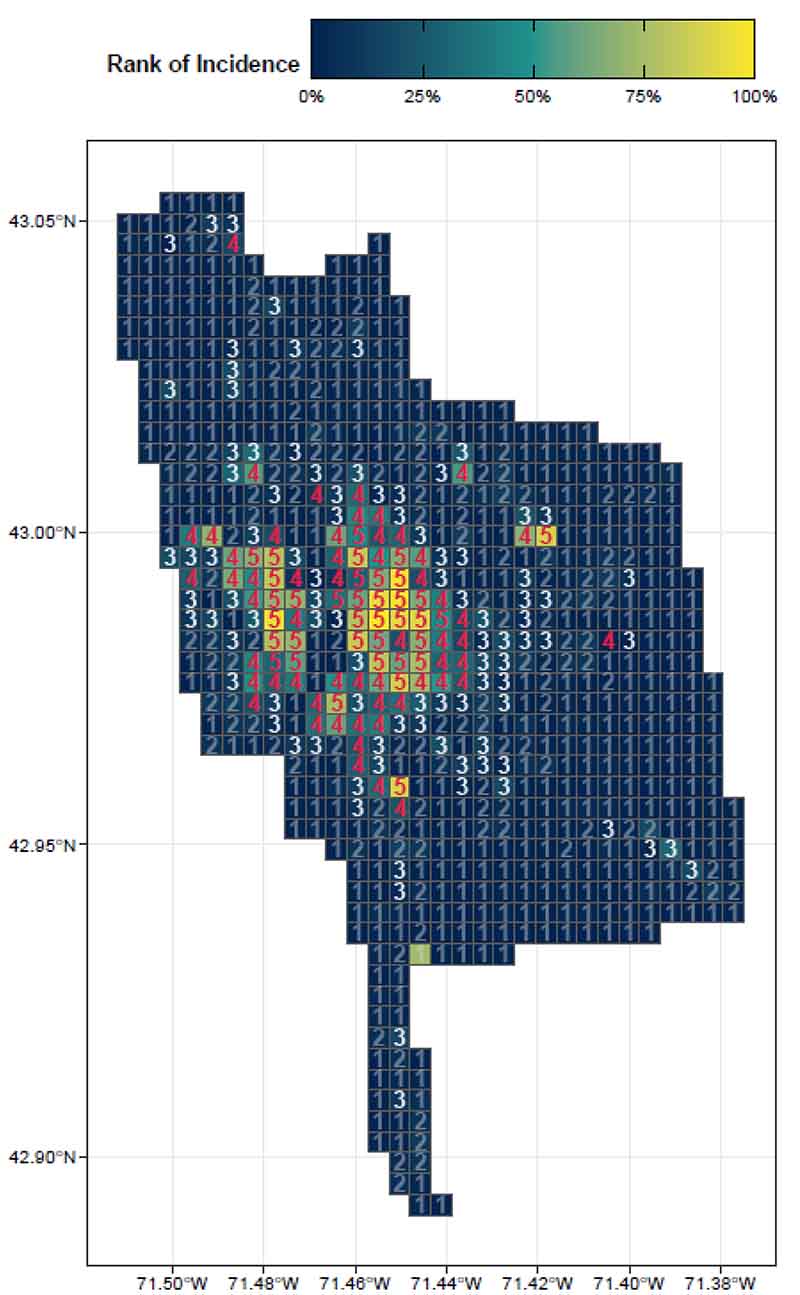
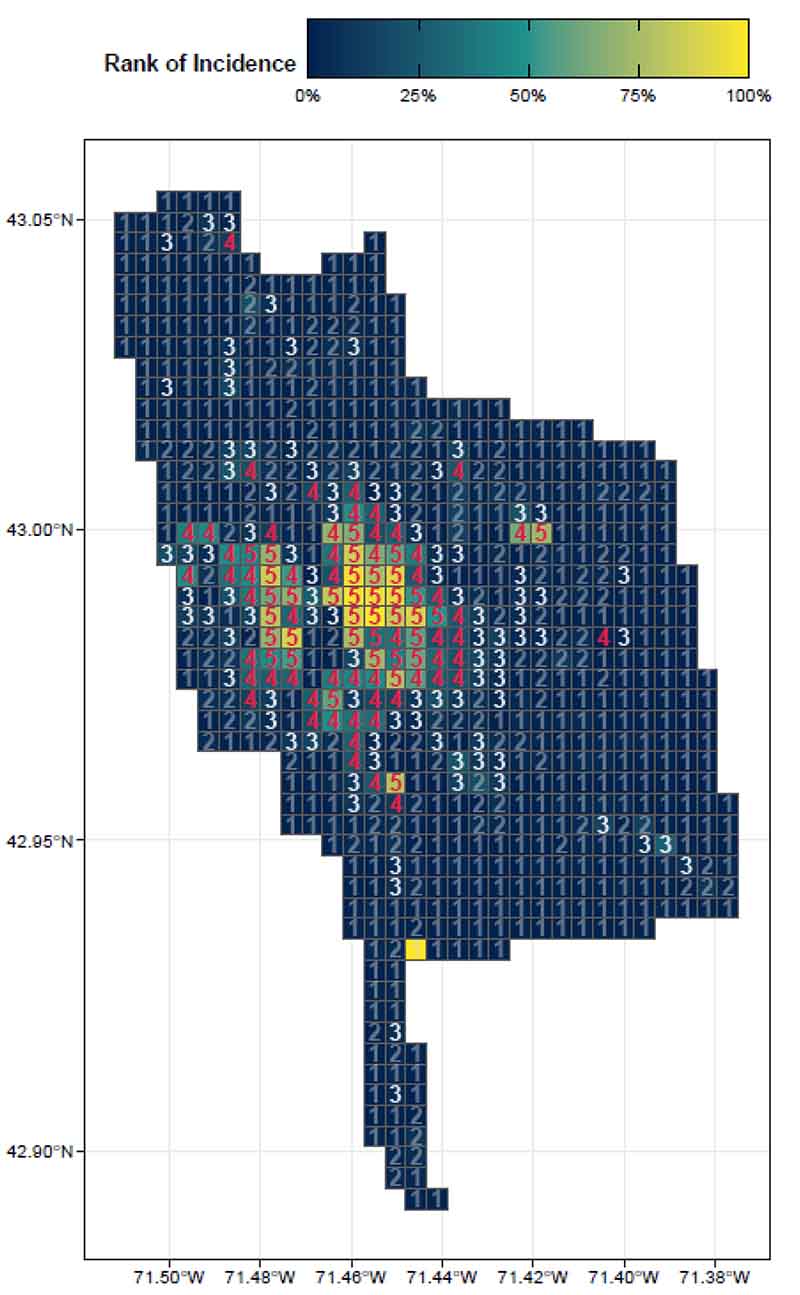
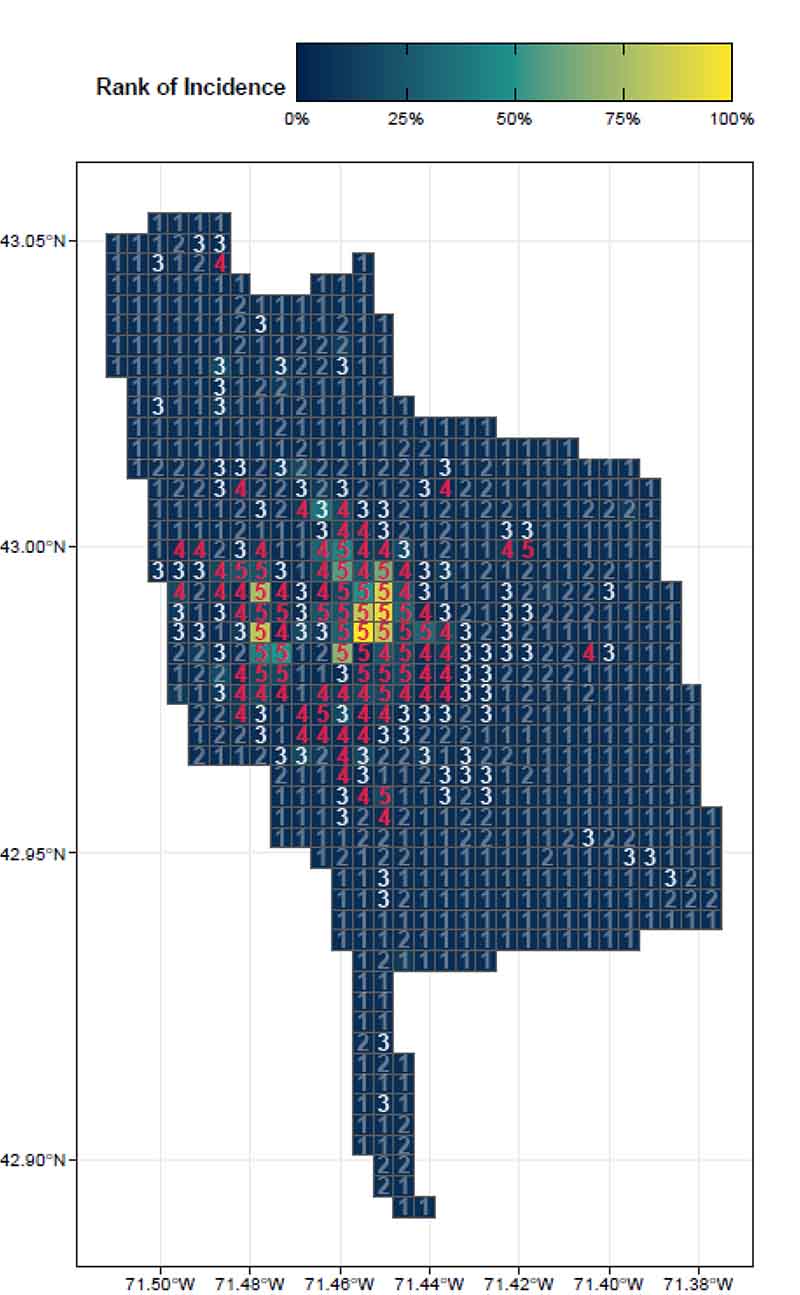
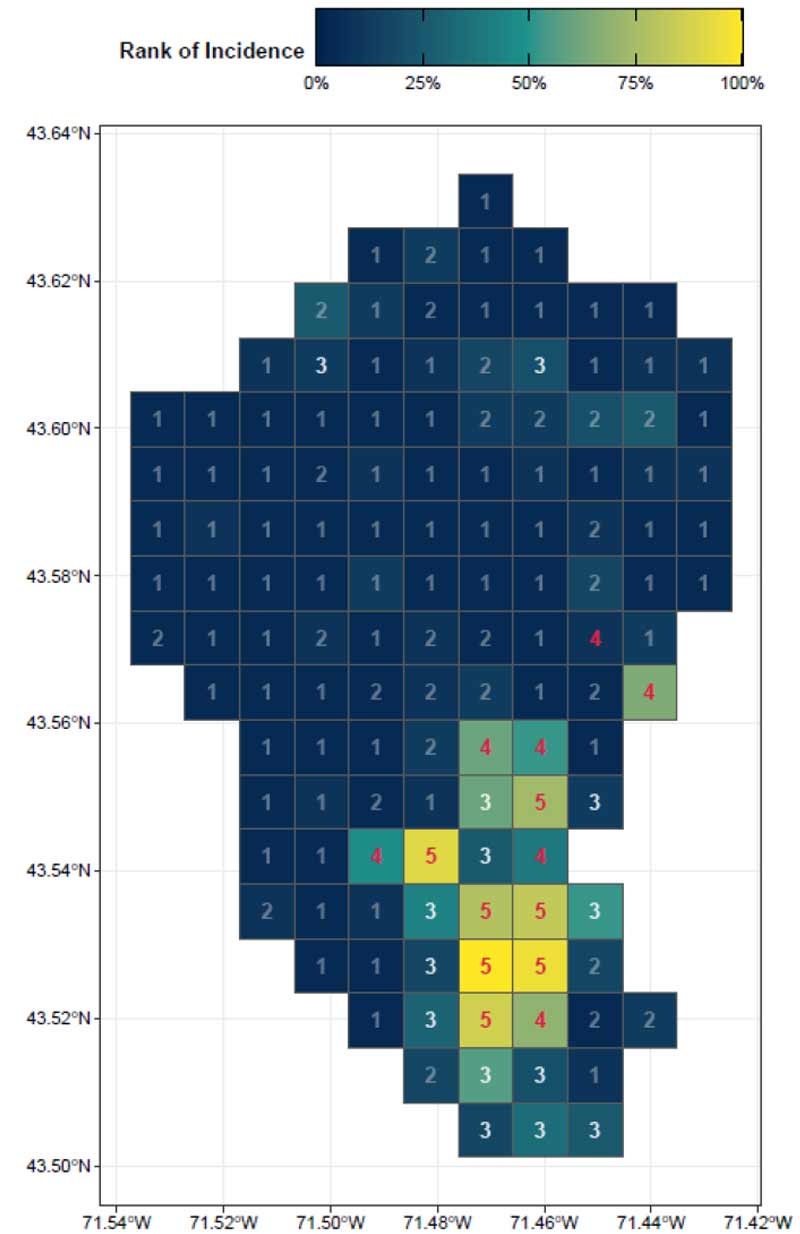
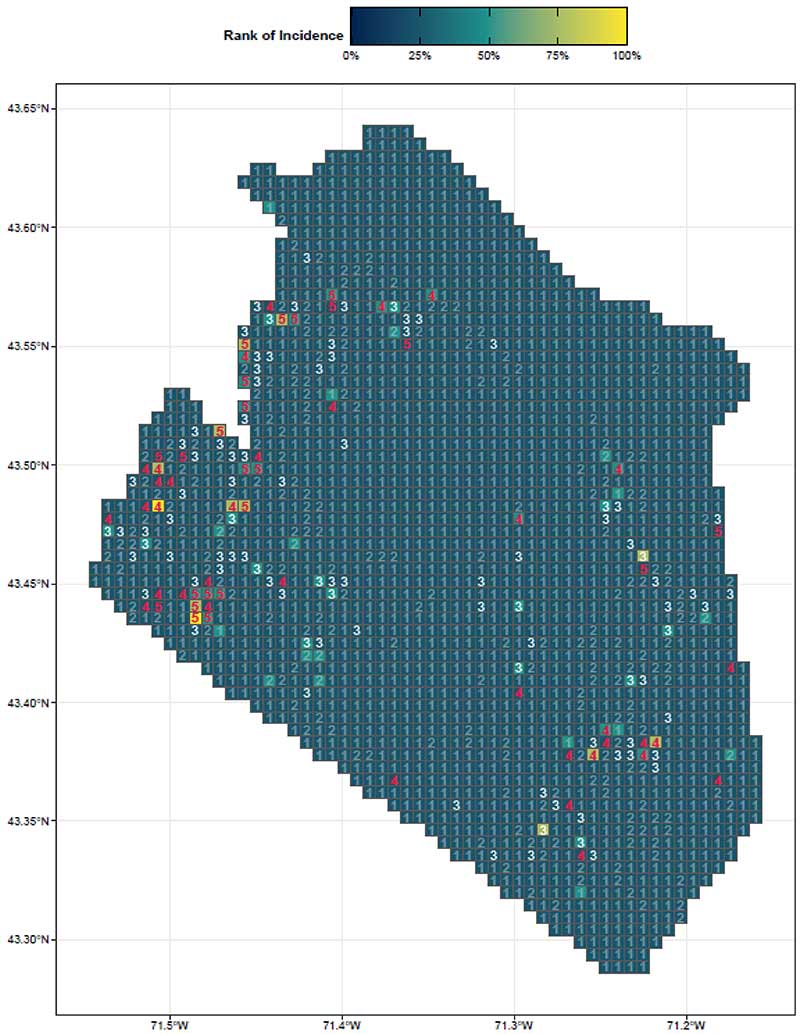
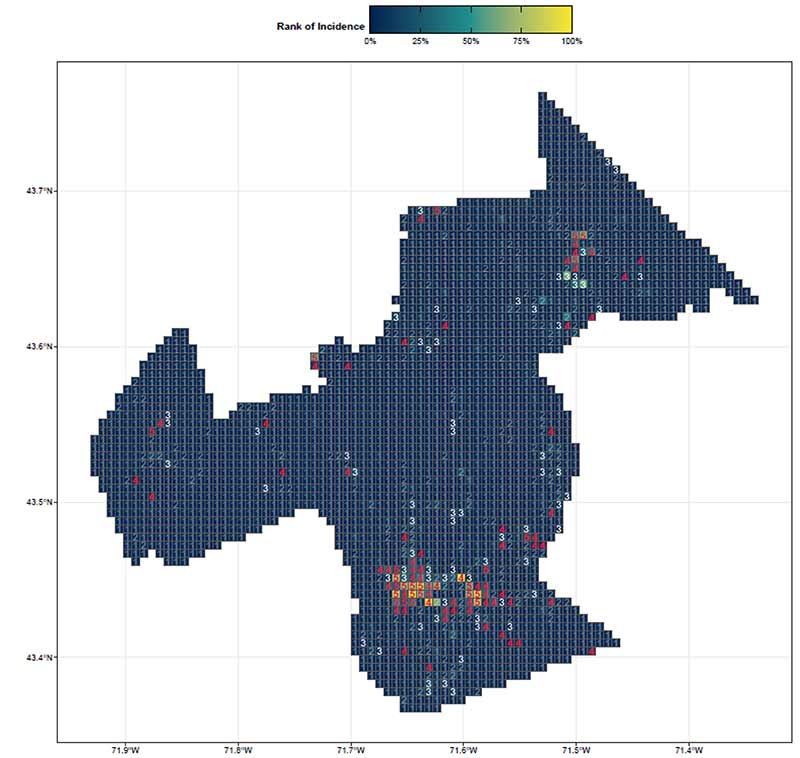
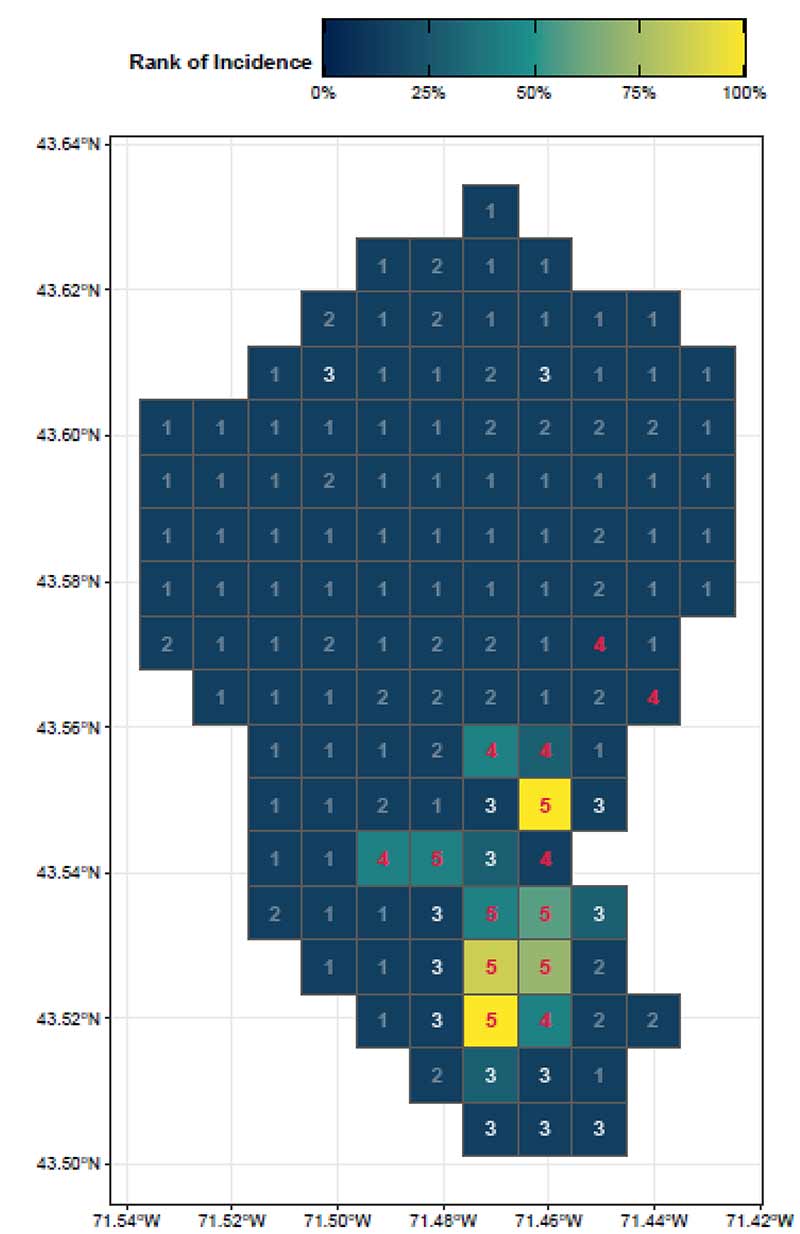
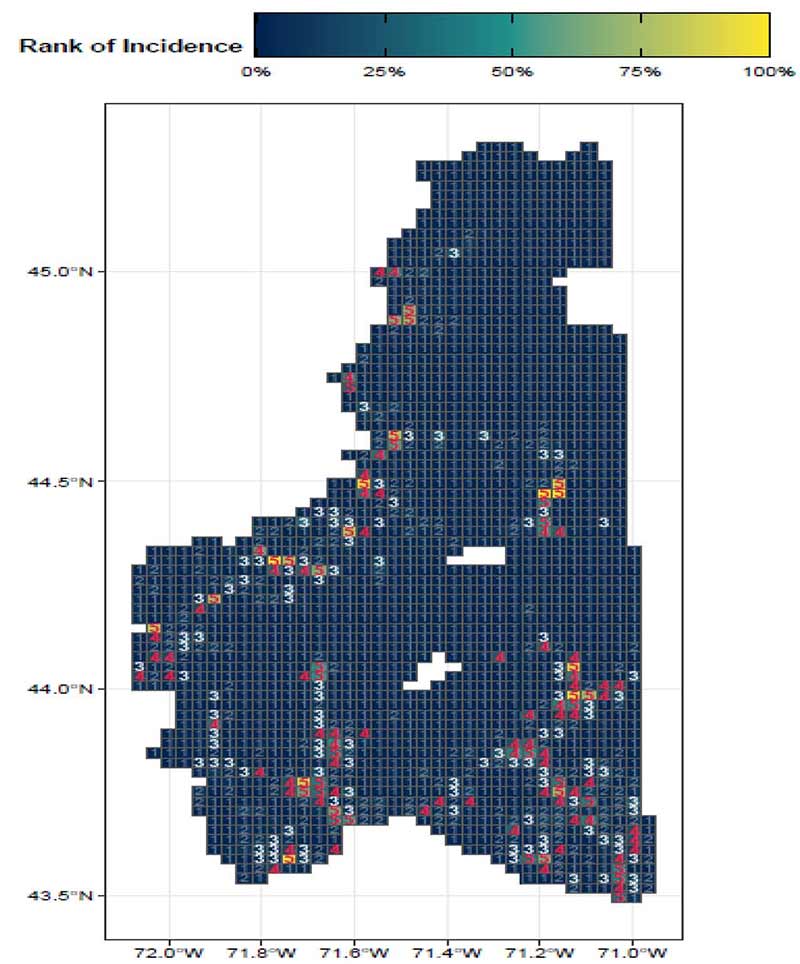
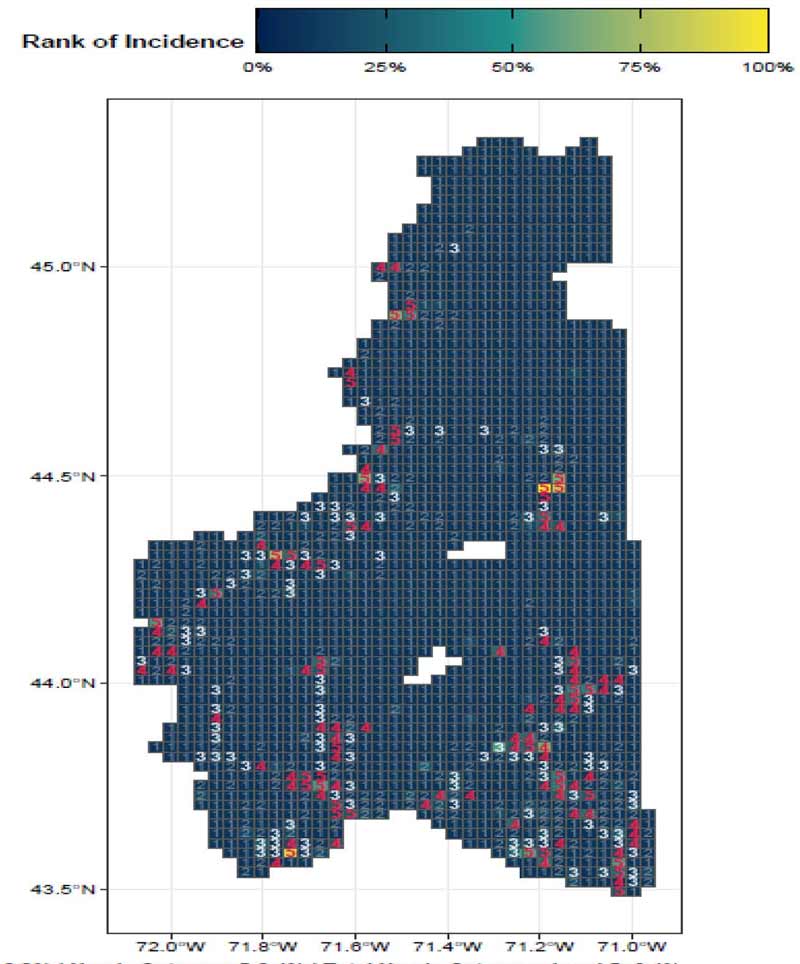
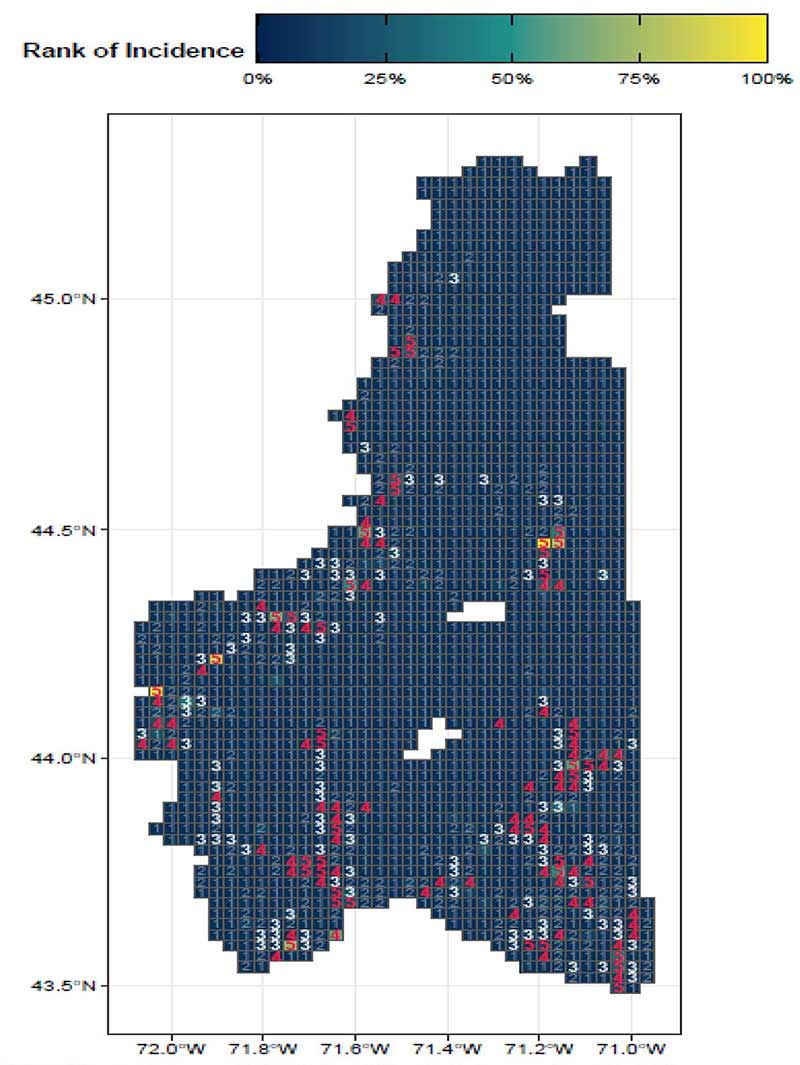
By focusing on this tradeoff, the final predictive model is able to produce highly targeted spatial risk predictions. These risk predictions are split into five risk categories, with five being the greatest risk.
These risk predictions can then be used to evaluate if the availability of child welfare services in a certain region is properly aligned with the demand for these services. This is done by embedding the risk predictions into a strategic planning framework that helps identify resources that are optimally located and can be used to decrease the risk of maltreatment. It is at these locations that stakeholders may wish to deploy education, outreach, and treatment programs.